Circuit Board Recycling Machine
With the rapid growth of electronic products, electronic waste has become one of the fastest-growing waste streams worldwide. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) contain valuable metals but are difficult to recycle using traditional methods. circuit board recycling machine provides an efficient, environmentally friendly, and profitable solution for recovering resources from waste circuit boards.
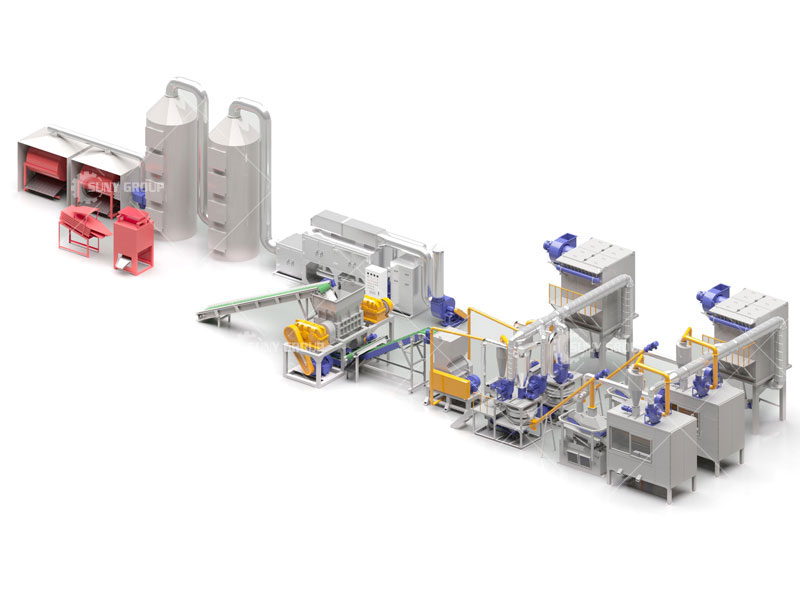
1. What Is a Circuit Board Recycling Machine
Circuit board recycling machine is a specialized system designed to process waste printed circuit boards and separate valuable metals from non-metal materials. These machines are widely used in e-waste recycling plants, metal recovery facilities, and environmental protection projects. By combining mechanical crushing and physical separation technologies, the machine can efficiently recover copper and other metals while minimizing environmental pollution. Compared with manual dismantling or chemical methods, circuit board recycling machines offer higher efficiency, safer operation, and better material purity.
2. Working Principle of a Circuit Board Recycling Machine
The working principle of a circuit board recycling machine is mainly based on mechanical size reduction and physical separation. First, waste circuit boards are fed into a shredder or crusher, where they are broken into smaller pieces. These pieces are further ground into fine particles using a hammer mill or pulverizer. After crushing, the mixed materials enter separation systems such as air classifiers, gravity separators, or electrostatic separators. Since metals and non-metals have different densities and electrical conductivity, they can be effectively separated without using chemicals, ensuring an eco-friendly recycling process.
3. Recycling Process Flow of Circuit Boards
The recycling process of circuit boards follows a standardized and continuous workflow. It typically starts with feeding and primary shredding, where large PCBs are reduced in size. Next comes secondary crushing and grinding, producing uniform particles suitable for separation. The third stage is multi-stage separation, where copper, aluminum, and other metals are separated from resin and fiberglass powder. Finally, dust collection and material output ensure clean operation and high recovery rates. This automated process improves productivity and makes large-scale circuit board recycling possible.
4. Recovered Materials and Their Applications
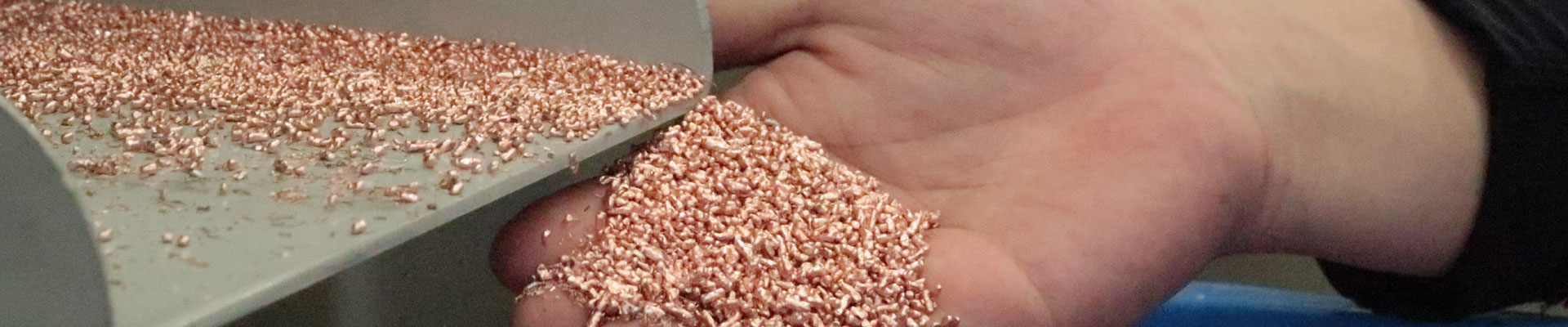
A circuit board recycling machine can recover several valuable materials. The most important is copper, which can reach a recovery purity of over 99% and is widely used in cable manufacturing, electrical components, and metal smelting. Small amounts of aluminum and iron can also be recovered for reuse in metal processing industries. The non-metal fraction, mainly resin powder and fiberglass, can be reused as fillers in construction materials, insulation products, or composite boards. This high material utilization rate makes circuit board recycling both economically and environmentally beneficial.
5. Market Trends and Investment Potential
Driven by stricter environmental regulations and the growing volume of e-waste, the global demand for circuit board recycling machines continues to rise. Many countries now encourage formal e-waste recycling through policy support and subsidies. For investors, circuit board recycling offers stable raw material supply, high metal recovery value, and long-term market growth. Compared with traditional mining, recycling circuit boards requires lower energy consumption and investment, making it an attractive opportunity in the circular economy.
Circuit board recycling machine plays a crucial role in modern e-waste management. With advanced working principles, efficient recycling processes, and high-value material recovery, it provides a sustainable solution to electronic waste challenges. As environmental awareness and market demand increase, investing in circuit board recycling technology will continue to show strong economic and ecological returns.


